If price floor is less than market equilibrium price then it has no impact on the economy.
A price floor set below the equilibrium price.
Drawing a price floor is simple.
If set below the equilibrium price it would have no effect.
If it s not above equilibrium then the market won t sell below equilibrium and the price floor will be irrelevant.
This is the currently selected item.
Have no impact on the equilibrium price and quantity.
This graph shows a price floor at 3 00.
Once introduced at pmin the price floor will cause an excess supply surplus of q3 q1 because quantity demanded is q1 and quantity supplied is q3.
Producers won t produce as much at the lower price while consumers will demand more because the goods are cheaper.
However price floor has some adverse effects on the market.
For a price floor to be effective it must be set above the equilibrium price.
When a price floor is set above the equilibrium price quantity supplied will exceed quantity demanded and excess supply or surpluses will result.
As seen in the diagram minimum price is set above the market equilibrium price.
Price and quantity controls.
Price floors prevent a price from falling below a certain level.
Price floors prevent a price from falling below a certain level.
Minimum wage and price floors.
In this case the floor has no practical effect.
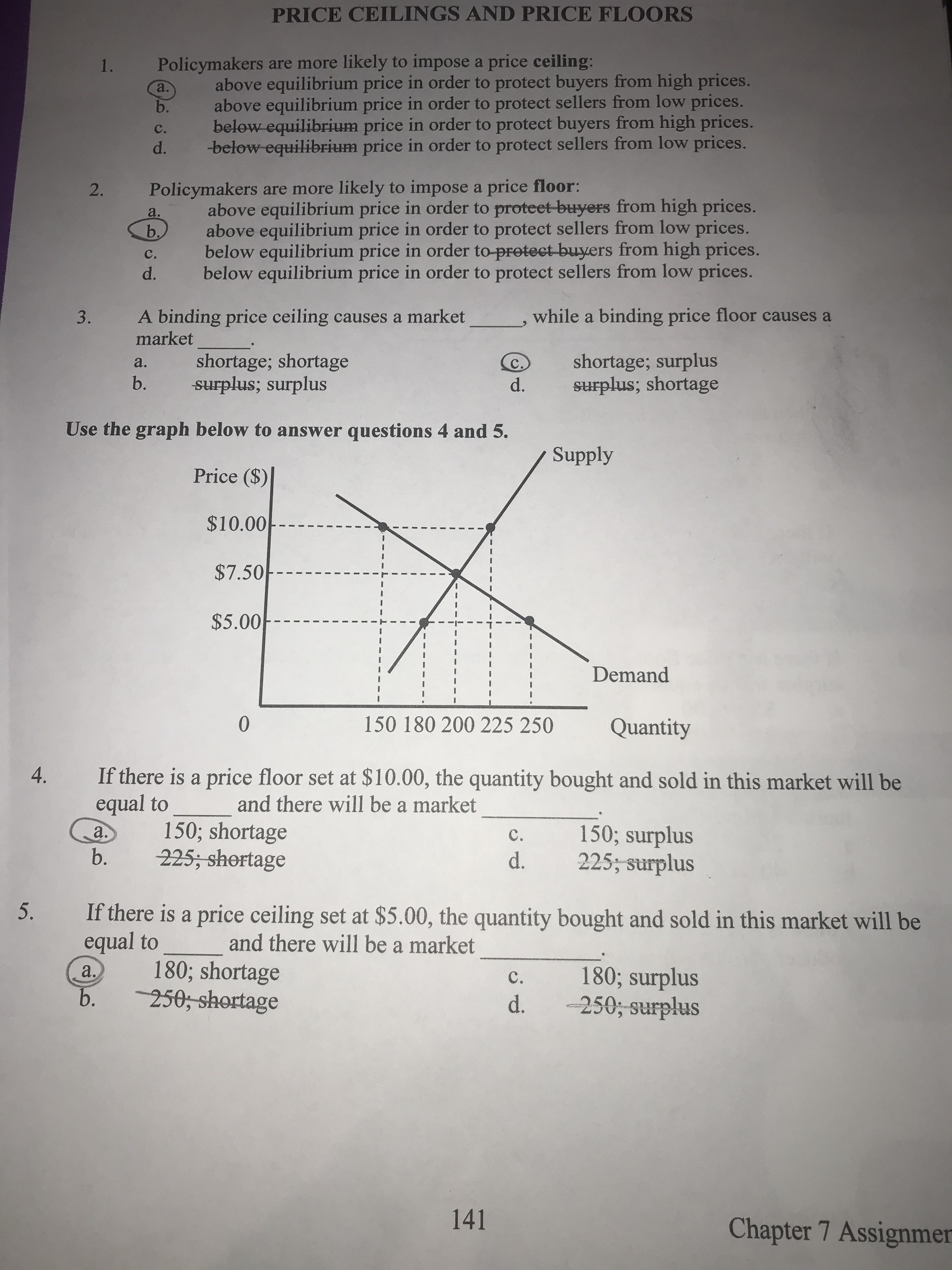
Price ceilings and price floors.
In the figure given below a price floor set at 20 00 will.
Example breaking down tax incidence.
When a price floor is set above the equilibrium price quantity supplied will exceed quantity demanded and excess supply or surpluses will result.
A price floor could be set below the free market equilibrium price.
Price floor is enforced with an only intention of assisting producers.
Taxation and dead weight loss.
Government set price floor when it believes that the producers are receiving unfair amount.
Price floors and price ceilings often lead to unintended consequences.
When the ceiling is set below the market price there will be excess demand or a supply shortage.
Effects of a price floor on different stakeholders.
The government has mandated a minimum price but the market already bears and is using a higher price.
Price floors and price ceilings often lead to unintended consequences.
Price ceilings only become a problem when they are set below the market equilibrium price.
The effect of government interventions on surplus.
In the first graph at right the dashed green line represents a price floor set below the free market price.